Refresh rate is one of the most significant display specifications that directly impacts how smooth and responsive your mobile phone feels during daily use. As smartphones have evolved from basic communication devices into powerful multimedia and gaming platforms, understanding refresh rate has become essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
The refresh rate determines how fluid animations appear, how responsive scrolling feels, and how immersive your gaming experience becomes. While 60Hz was the standard for years, modern smartphones increasingly feature higher refresh rates of 90Hz, 120Hz, 144Hz, or even 165Hz, fundamentally changing how we interact with our devices.
Definition of Refresh Rate
Refresh rate refers to the number of times per second that a display updates its image, measured in Hertz (Hz). This measurement represents how frequently the screen can draw new frames, creating the visual content you see.
Common refresh rate specifications and their meanings:
- 60Hz: The screen refreshes 60 times per second, displaying 60 frames per second
- 90Hz: Updates 90 times per second, providing 50% more frames than 60Hz
- 120Hz: Refreshes 120 times per second, exactly double the standard 60Hz rate
- 144Hz: Updates 144 times per second, commonly found in gaming-focused smartphones
- 165Hz: The emerging ultra-high refresh rate being researched by manufacturers like REDMI
Each increment in refresh rate reduces the time between frame updates. For example, a 60Hz display takes 16.6 milliseconds to refresh completely, while a 120Hz panel requires only 8.3 milliseconds. This reduction in refresh time contributes to lower display latency and more responsive user interactions.
How Refresh Rate Works on Mobile Phones
Mobile phone displays update images through a continuous cycle of refreshing frames per second. The display controller coordinates with the graphics processor to draw each frame sequentially, creating the illusion of smooth motion when viewed by the human eye.
The fundamental difference between low and high refresh rates becomes apparent in daily usage scenarios:
Scrolling Experience: At 60Hz, scrolling through social media feeds, web pages, or app menus can appear slightly choppy, especially during rapid movements. Higher refresh rates like 90Hz or 120Hz make scrolling feel dramatically smoother and more natural.
Gaming Performance: Mobile games benefit significantly from higher refresh rates. Fast-paced action games, racing simulators, and competitive multiplayer titles display more fluid character movements and reduced motion blur at 120Hz compared to 60Hz. However, the game itself must support the higher frame rate to realize these benefits.
Video Playback: While most videos are recorded at 24fps or 30fps, higher refresh rates can still improve the viewing experience through better frame interpolation and reduced judder during camera movements.
General Navigation: Everyday interactions like opening apps, switching between screens, and using gesture controls feel more responsive and immediate with higher refresh rates.
Typical refresh rates available in modern mobile devices include:
- 60Hz: Still standard in budget smartphones and older flagship models like iPhone 14 base models
- 90Hz: Common in mid-range devices, offering a noticeable improvement over 60Hz
- 120Hz: Widely adopted in premium smartphones including iPhone 15 Pro, Samsung Galaxy S24, and most flagship Android devices
- 144Hz: Found in gaming-focused smartphones like ASUS ROG series and some OnePlus models
- 165Hz: Emerging as the next frontier, with manufacturers like REDMI researching implementation
Evolving trends show that higher refresh rates are filtering down from premium gaming phones to mainstream devices. The smartphone industry follows a similar pattern to computer monitors, where features initially exclusive to high-end products eventually become standard across all price segments.
The user experience difference is most pronounced in the jump from 60Hz to 90Hz, with diminishing returns at higher refresh rates. Many users report that while the improvement from 120Hz to 144Hz is measurable, it’s less dramatic than the initial upgrade from standard 60Hz to 90Hz.
Benefits of Higher Refresh Rates
Smoother Visuals and Animations: Higher refresh rates provide significantly improved visual fluidity. Every animation, transition, and movement appears more natural and lifelike. Scrolling through apps, switching between screens, and navigating menus feels dramatically more responsive compared to traditional 60Hz displays.
Enhanced Gaming Experience: Mobile gaming receives substantial benefits from higher refresh rates. Competitive games like PUBG Mobile, Call of Duty Mobile, and racing games display smoother character movements, more precise aiming responsiveness, and clearer visibility during fast-paced action sequences. The increased frame rate provides gamers with a competitive advantage through improved reaction times and reduced visual lag.
Reduced Motion Blur and Better Responsiveness: Higher refresh rates minimize motion blur that occurs when fast-moving objects appear blurry due to display limitations. This reduction is particularly beneficial for activities requiring visual clarity during motion, such as reading while scrolling, watching action videos, or tracking moving objects in games. The faster pixel response times also contribute to more immediate touch responsiveness.
Improved Touch Interface Response: Displays with higher refresh rates exhibit faster response times between touch input and visual feedback. This enhanced responsiveness is crucial for activities like typing, where quick and accurate responses to finger inputs significantly improve the user experience.
Drawbacks and Considerations
Impact on Battery Life: The most significant drawback of higher refresh rates is increased power consumption. Research shows that enabling 120Hz on Samsung Galaxy S20 devices reduces battery life by 20-36% compared to 60Hz operation. The display processor and graphics unit must work harder to generate and display more frames per second, directly correlating to faster battery drain.
Hardware Requirements: High refresh rate displays demand more powerful hardware components. The graphics processing unit must generate sufficient frames per second to match the display’s capability, requiring more robust chipsets and increased RAM to handle the additional computational load. Budget smartphones may struggle to consistently maintain high refresh rates across all applications.
Interplay with Screen Resolution and Performance: Many early high refresh rate smartphones required users to choose between maximum resolution and highest refresh rate. While newer flagship devices can maintain both 1440p resolution and 120Hz simultaneously, this combination still demands significant processing power and battery resources. The relationship between refresh rate, resolution, and overall device performance requires careful optimization by manufacturers.
Content Limitations: Most mobile content, including videos and many apps, doesn’t natively support refresh rates above 60Hz. Users may not experience the full benefits of their high refresh rate display when consuming standard media content or using applications not optimized for higher frame rates.
How to Check and Change Refresh Rate Settings
For Android Devices (Samsung Galaxy, OnePlus and iPhone):
Samsung Galaxy Phones:
1. Open Settings and select Display
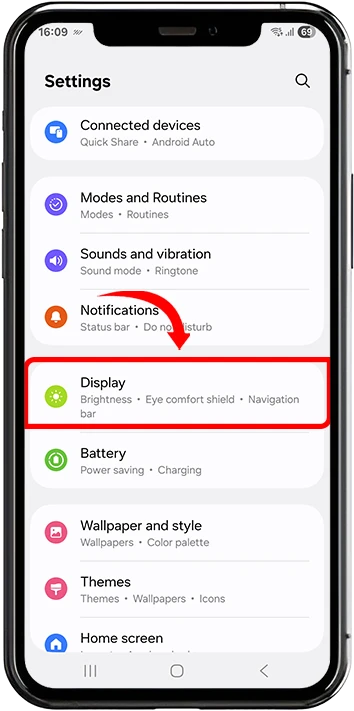
2. Tap Motion smoothness
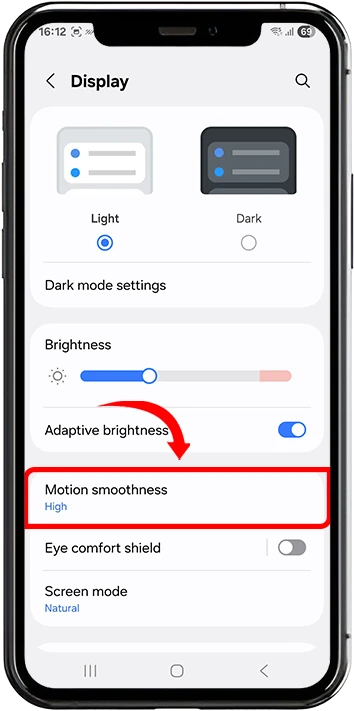
3. Choose between Standard (60Hz) or High (90HZ/120Hz) depending on your device capabilities
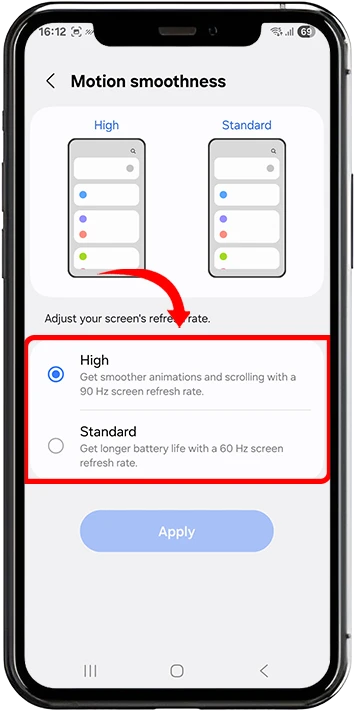
4. Confirm your selection and restart if prompted
OnePlus Phones:
1. Navigate to Settings > Display and Brightness
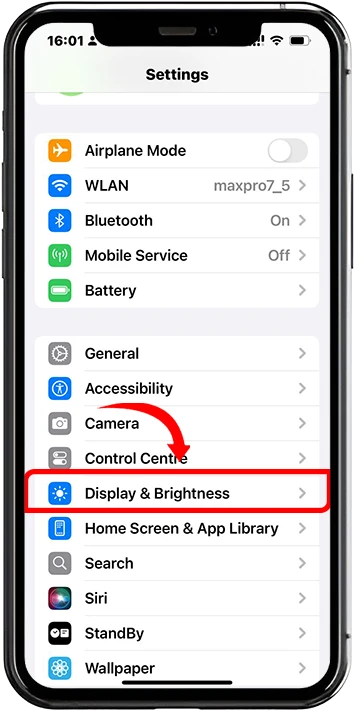
2. Look for options like Screen Refresh Rate
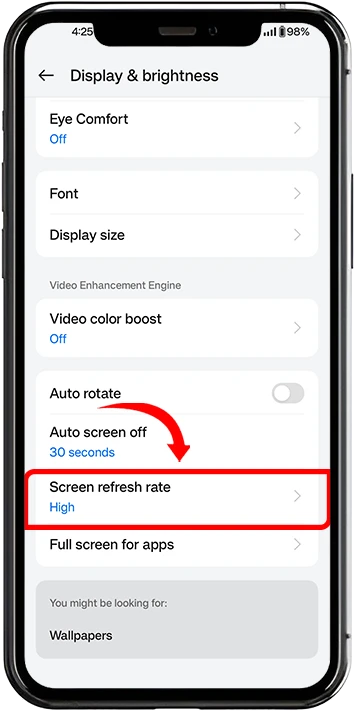
3. Select from available options (typically 60Hz, 90Hz, or 120Hz)
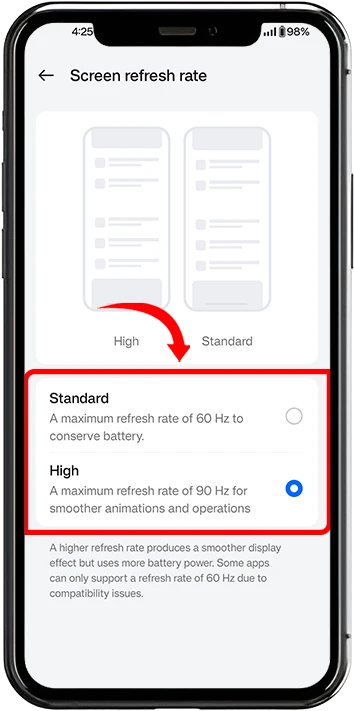
4. Apply settings and observe the immediate difference in smoothness
iPhone
iPhone and newer models with ProMotion:
1. Open Settings and go to Accessibility
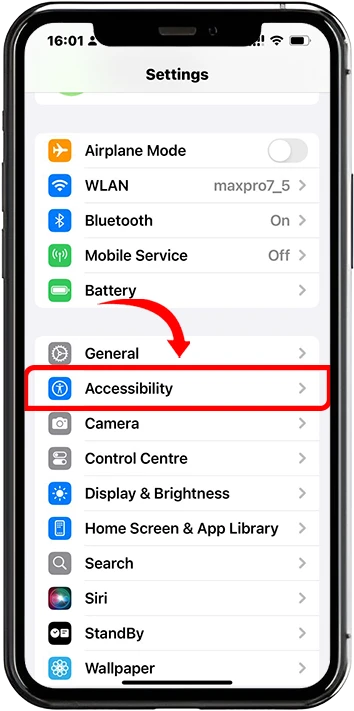
2. Select Motion from the accessibility options
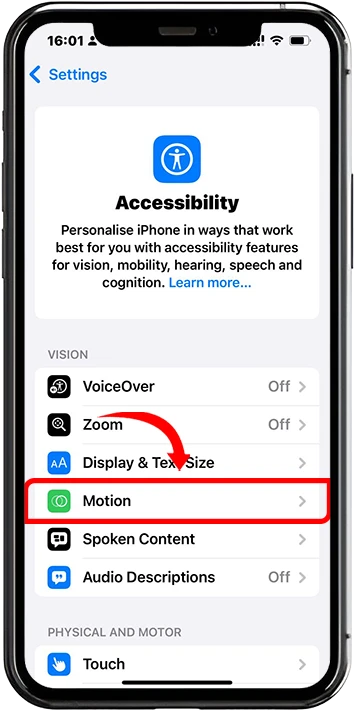
3. Toggle switch on to Reduce Motion
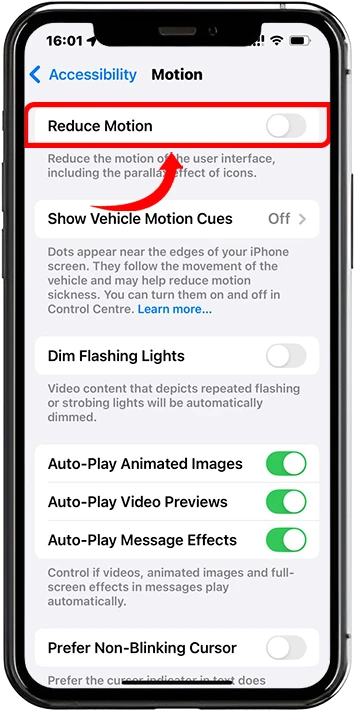
4. When disabled, the phone operates at maximum Frequency and When enabled, the phone limits the Frequency for battery conservation.








