| Image | Name | Short Description |
|---|---|---|
| AC Voltage Source | An ideal source of Alternating Current (AC) voltage. It produces a voltage that continuously changes polarity, typically in a sinusoidal waveform. This represents the standard form of electricity from wall outlets. | |
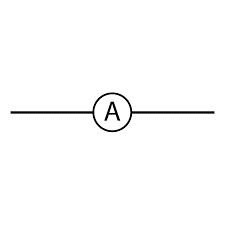 |
Ammeter | An instrument used for measuring the electric current in a circuit. The current to be measured must flow directly through the ammeter, so it is connected in series with the circuit. |
| AND Gate | A basic digital logic gate. Its output is HIGH (1) only if all of its inputs are HIGH (1). If any input is LOW (0), the output will be LOW. | |
 |
Antenna / Aerial | A device designed to transmit or receive radio waves. It converts electrical power into radio waves (transmitter) or radio waves into electrical power (receiver). It is a fundamental component in wireless communication. |
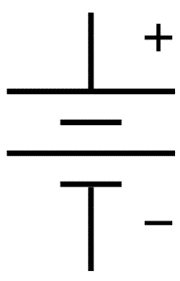 |
Battery | A power source that converts stored chemical energy into direct current (DC) electrical energy. It consists of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections to power electrical devices. |
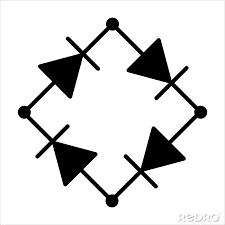 |
Bridge Rectifier | An arrangement of four diodes in a bridge configuration that provides full-wave rectification of an AC input. It converts both the positive and negative halves of the AC cycle into a pulsating DC output. |
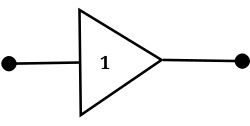 |
Buffer | A digital logic gate that does not perform a logical operation. Its output state is the same as its input state. It is used to amplify a weak signal and provide higher current drive capability. |
| Capacitor (Non-polarized) | A passive component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. Non-polarized capacitors can be connected in either direction in a circuit and are commonly used in AC signals, filtering, and timing applications. | |
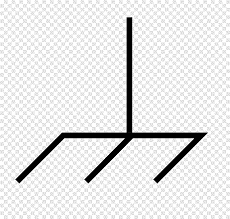 |
Chassis Ground | Represents a connection to the metal frame or chassis of the equipment. It is used for safety and shielding, providing a common return path for current and protecting against internal faults and external interference. |
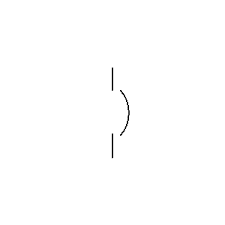 |
Circuit Breaker | An automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect a circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Unlike a fuse, it can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation once the fault is cleared. |
 |
Coaxial Cable | A type of shielded cable with a central conductor surrounded by a tubular insulating layer, which is then surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. Widely used for television signals, internet, and radio frequency feeds. |
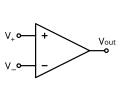 |
Comparator | A device that compares two input voltages and outputs a digital signal indicating which is larger. It is similar to an op-amp but is designed for open-loop operation and fast switching. |
| Connected Wires | Represents two or more wires that are physically and electrically joined together at a point called a node. This connection allows current to flow from one wire to the other, ensuring continuity in the circuit. | |
| Controlled Current Source | A dependent current source whose output current is determined by either a voltage or a current in another part of the circuit. It is used to model the behavior of active devices like transistors. | |
| Controlled Voltage Source | A dependent voltage source whose output voltage is controlled by either another voltage or current elsewhere in the circuit. Its value is not fixed but is a function of another signal in the network. | |
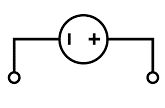
| Current Source | An ideal source that provides a constant, specified current to a circuit, regardless of the voltage across its terminals. It is a fundamental concept used in circuit analysis and modeling. | |
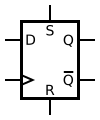 |
D Flip-Flop | A type of flip-flop that captures the value of the D (Data) input at the moment a clock signal transitions. It is a fundamental building block for digital memory, registers, and counters. |
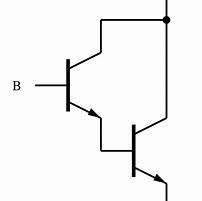 |
Darlington Transistor | A configuration of two bipolar transistors connected to provide very high current gain. A tiny base current results in a very large emitter-collector current. Used where high sensitivity is needed, like in touch sensors. |
 |
DC Motor | A motor that runs on Direct Current (DC) electricity. Its speed can be controlled by varying the supply voltage. Used in applications ranging from toys to industrial machinery. |
 |
DC Voltage Source | An ideal source of constant Direct Current (DC) voltage. It maintains a fixed voltage level across its terminals regardless of the current drawn by the load. It is a simplified model for power supplies and batteries. |
 |
Demultiplexer / Demux | A combinational logic circuit that takes a single input signal and routes it to one of several output lines. The selection of which output gets the signal is controlled by a separate set of select lines. |
| Diode | A semiconductor device that allows current to flow easily in one direction (forward bias) and blocks it in the opposite direction (reverse bias). It is used for rectification, protection, and signal demodulation. | |
| DIP Switch | A Dual In-line Package switch, which is a set of small manual switches in a single block designed to be mounted on a circuit board. Used for configuration settings, like setting device addresses or modes. | |
 |
Dipole Antenna | The simplest and most widely used type of antenna. It consists of two identical conductive elements, with the signal fed between them. Its length is typically half the wavelength of the frequency it is designed for. |
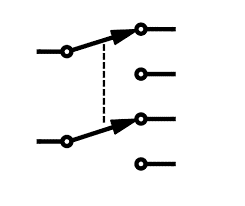 |
DPDT Switch | A Double-Pole, Double-Throw switch. It is equivalent to two SPDT switches operating together from a single actuator. It can control two circuits, each routed to one of two different outputs. |
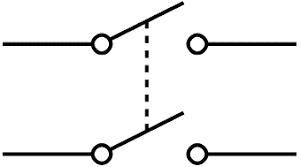 |
DPST Switch | A Double-Pole, Single-Throw switch. It acts like two separate SPST switches controlled by a single mechanism. It can simultaneously control two independent circuits, turning them both on or off together. |
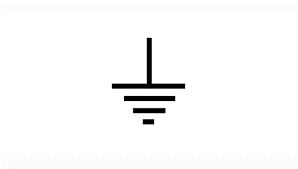 |
Earth / Ground | Also known as “true earth,” this symbol represents a direct physical connection to the earth, which is considered to be at zero voltage potential. It is used for safety to prevent electric shock. |
| Electric Bell | A mechanical bell that functions by means of an electromagnet. When current is applied, the electromagnet pulls a clapper to strike the bell, and a spring returns it, often creating a continuous ring. | |
| Electrical Wire | A conductor that provides a path for electrical current to flow. It is the most basic component, connecting all others in a circuit. Wires are typically made of copper or aluminum and are insulated with a non-conductive coating to prevent short circuits. | |
 |
Fiber Optic Cable | A cable containing one or more optical fibers that carry light. Used for high-speed data transmission over long distances, as it is immune to electromagnetic interference and has very low signal loss. |
 |
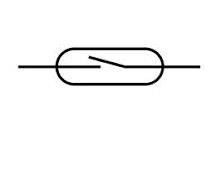
Fuse | A safety device that protects an electrical circuit from overcurrent. It contains a metal wire that melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a specified rating for a certain time, preventing damage to other components. |
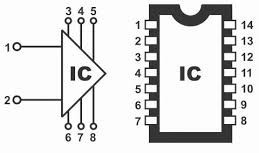 |
General IC Symbol | Represents an Integrated Circuit (IC) or “chip.” It is a complete circuit containing many components like transistors, resistors, and diodes fabricated on a small piece of semiconductor material. |
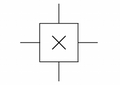 |
Hall Effect Sensor | A transducer that varies its output voltage in response to a magnetic field. It is used for proximity switching, positioning, speed detection, and current sensing applications. |
 |
Headphones | A pair of small loudspeakers worn on or around the head over a user’s ears. They are electroacoustic transducers which convert an electrical signal to a corresponding sound. |
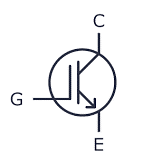 |
IGBT Transistor | An Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistor combines the simple gate drive of a MOSFET with the high-current and low-saturation-voltage capability of a BJT. It is used in high-power applications like motor drives and inverters. |
 |
Inductor (Coil) | A passive component that stores energy in a magnetic field when current flows through it. It resists changes in current, making it useful in filtering, tuning circuits, and power supplies. It is essentially a coil of wire. |
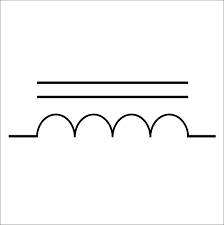 |
Iron Core Inductor | An inductor that has a core made of a ferromagnetic material like iron or ferrite. This core significantly increases the inductance value by concentrating the magnetic field, allowing for a smaller physical size for a given inductance. |
| JFET (N-channel) | A Junction Field-Effect Transistor. The N-channel JFET is normally on (conducting), and a voltage applied between the gate and source that depletes the channel is used to reduce the current flow. | |
| JFET (P-channel) | A JFET that uses P-type semiconductor material. It is normally on, and a positive gate-source voltage is used to control and reduce the current through the device. | |
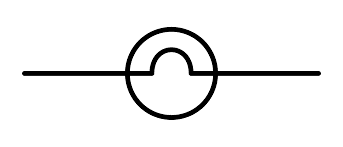 |
Lamp / Light Bulb | A transducer that converts electrical energy into light energy. In schematics, it can also represent an indicator light or a small incandescent, fluorescent, or LED-based illumination device. |
 |
Laser Diode | Similar to an LED but produces coherent, monochromatic light through stimulated emission. It is the core component in laser pointers, fiber optic communication, barcode readers, and DVD/CD drives. |
 |
LCD Display Block | Represents a Liquid Crystal Display module. It is a flat-panel display that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals. It can display custom characters, graphics, or text. |
| LDR / Photoresistor | A Light Dependent Resistor. Its electrical resistance decreases when the intensity of light incident on it increases. It is used in light-sensing applications like automatic street lights and camera light meters. | |
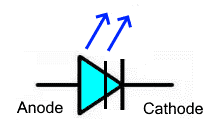
| Light Emitting Diode (LED) | A diode that emits light when current flows through it in the forward direction. The color of the light depends on the semiconductor material used. Used for indicators, displays, and lighting. | |
 |
Loop Antenna | A radio antenna consisting of a loop or coil of wire. They are particularly useful for receiving directional signals and are often used in AM radios and direction-finding equipment. |
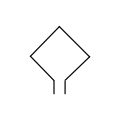
| Loudspeaker / Speaker | A transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into sound waves. It does this by causing a diaphragm to vibrate, which in turn vibrates the air to create sound. | |
| Microphone | An acoustic sensor that converts sound waves into an electrical signal. The varying air pressure of the sound wave is transformed into a corresponding varying voltage. | |
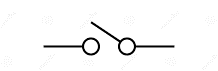 |
Microswitch | A type of snap-action switch that requires very little physical force to activate. It is known for its precise operation and audible “click,” commonly used in limit switches, door interlocks, and vending machines. |
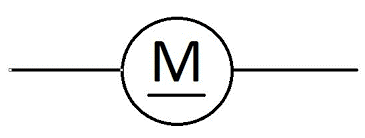 |
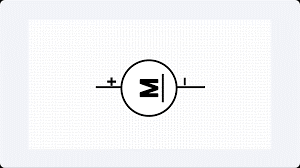
Motor | A general symbol for an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy (rotation). It operates through the interaction between a magnetic field and electric current in a coil to produce torque. |
 |
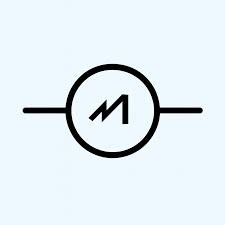
Multimeter | A versatile electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter can measure voltage (volts), current (amps), and resistance (ohms). |
 |
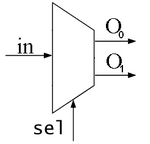
Multiplexer / Mux | A combinational logic circuit that selects one of several input signals and forwards the selected input to a single output line. The selection is controlled by a separate set of select lines. |
| NAND Gate | A universal logic gate. Its output is LOW (0) only if all of its inputs are HIGH (1). For all other input combinations, the output is HIGH (1). It is an AND gate followed by a NOT gate. | |
| NMOS Transistor | A type of Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET). It turns on when a positive voltage is applied to the gate relative to the source. It uses electrons as the primary charge carriers. | |
| NOR Gate | A universal logic gate. Its output is HIGH (1) only when all of its inputs are LOW (0). For all other input combinations, the output is LOW (0). It is an OR gate followed by a NOT gate. | |
| Not Connected Wires | Depicts two wires that cross over each other in a diagram without being electrically connected. This is a crucial distinction to prevent misinterpretation of the circuit layout. A small bridge or gap is often shown to emphasize the lack of connection. | |
| NOT Gate (Inverter) | A digital logic gate with a single input. It performs the operation of logical negation. It outputs a HIGH (1) if the input is LOW (0), and a LOW (0) if the input is HIGH (1). | |
| NPN Bipolar Transistor | A type of bipolar junction transistor (BJT) where a small current entering the base controls a larger current between the collector and emitter. It turns on when the base is more positive than the emitter. | |
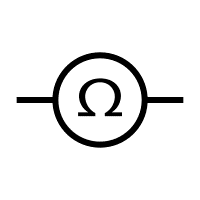 |
Ohmmeter | An instrument used for measuring the electrical resistance of a component or circuit. It operates by passing a known small current through the component and measuring the voltage drop across it. |
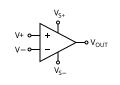 |
Operational Amplifier (Op-amp) | A high-gain voltage amplifier with a differential input and a single-ended output. It is a versatile “building block” used in a vast array of analog circuits, from filters to voltage comparators and signal conditioners. |
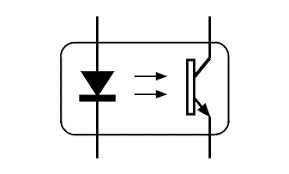 |
Optocoupler / Opto-Isolator | A component that transfers an electrical signal between two isolated circuits by using light. It contains an LED and a photosensor, providing excellent electrical isolation and noise immunity. |
| OR Gate | A basic digital logic gate. Its output is HIGH (1) if at least one of its inputs is HIGH (1). The output is LOW (0) only when all inputs are LOW. | |
 |
Oscilloscope Connection Symbol | Represents the input channel of an oscilloscope, an instrument that graphically displays varying electrical signals as a plot of voltage versus time. It is the primary tool for debugging electronic circuits. |
| Photodiode | A semiconductor device that converts light into an electrical current. It is operated in reverse bias, and the resulting current is proportional to the intensity of the incident light. Used in light sensors. | |
| Piezoelectric Buzzer / Buzzer | An audio signaling device that can be mechanical, electromechanical, or piezoelectric. Piezoelectric buzzers use a piezoelectric crystal to create a sound when a voltage is applied, commonly for alarms. | |
 |
Plug / Socket Connector | A component used to join electrical circuits together. A plug (male) is inserted into a socket or jack (female) to create a temporary, removable electrical connection for power or signals. |
| PMOS Transistor | A type of MOSFET that turns on when a negative voltage is applied to the gate relative to the source. It uses holes as the primary charge carriers. NMOS and PMOS are the building blocks of CMOS logic. | |
| PNP Bipolar Transistor | A BJT where a small current leaving the base controls a larger current flowing from the emitter to the collector. It turns on when the base is more negative than the emitter. | |
| Polarized Capacitor / Electrolytic Capacitor | A capacitor with a defined positive and negative terminal. It offers high capacitance values in a small package but must be connected with the correct polarity to prevent damage or failure. Commonly used for power supply filtering. | |
 |
Potentiometer | A three-terminal variable resistor. A voltage is applied across the two end terminals, and the middle wiper terminal provides a variable voltage output, functioning as a voltage divider. Commonly used for volume controls and sensors. |
| Potentiometer with Switch | A component that combines a potentiometer (for variable resistance/voltage) and a switch (typically SPST) in a single unit. Often found in audio equipment where turning the knob turns the device on and also adjusts volume. | |
| Push Button Switch (N.C.) | A momentary switch that is Normally Closed. The circuit is closed (on) when the button is not pressed. Pressing the button opens the circuit, and it springs back closed when released. | |
| Push Button Switch (N.O.) | A momentary switch that is Normally Open. The circuit is open (off) when the button is not pressed. Pressing the button closes the circuit, and it springs back open when released. | |
 |
Reed Switch | A switch operated by a magnetic field. It consists of two ferromagnetic reeds sealed in a glass tube. When a magnet is brought close, the reeds attract each other and make contact, completing the circuit. |
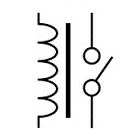 |
Relay (General) | An electrically operated switch. It uses a small current in one circuit (the coil) to control a larger current in another circuit (the contacts). It provides isolation between the control and load circuits. |
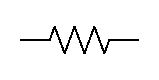 |
Resistor (IEEE/IEC) | A passive component that opposes the flow of electric current, converting some of it into heat. It is used to limit current, divide voltages, and adjust signal levels. The zigzag (IEEE) or rectangle (IEC) are two common symbolic representations. |
| Schottky Diode | A diode with a very low forward voltage drop and fast switching speed. It is constructed with a metal-semiconductor junction. Commonly used in high-frequency applications and power rectification for efficiency. | |
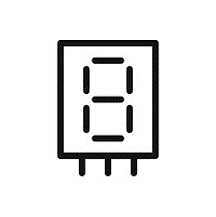 |
Seven-Segment Display | An electronic display device consisting of seven LEDs (segments) arranged in a figure-eight pattern. By illuminating different segments, it can display decimal digits and some letters. |
 |
Shielded Cable | A cable that has an outer conductive layer (shield) surrounding the inner signal-carrying conductor. This shield protects the signal from external electromagnetic interference (EMI) and contains the signal’s own EMI. |
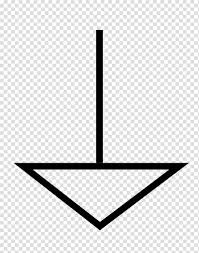 |
Signal / Digital / Common Ground | This symbol denotes a common reference point for voltage measurements in a circuit, particularly for signals. It is the “0V” reference, but it is not necessarily connected to the earth or chassis. |
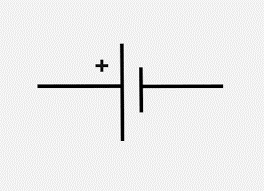 |
Single Cell / Battery Cell | The fundamental unit of a battery, producing a voltage via electrochemical reactions. Multiple cells are connected together in series or parallel to form a battery with higher voltage or capacity. |
| SPDT Relay | A SPDT relay (Single Pole Double Throw) is an electromechanical switch that controls one input circuit and can connect it to one of two output paths. It allows switching between two circuits, making it useful for selecting, routing, or alternating electrical signals. | |
| SPDT Switch | A Single-Pole, Double-Throw switch. It has one common input terminal and two output terminals. It can connect the common pole to either of the two other terminals, routing the signal to one of two paths. | |
| SPST Relay | A SPST relay (Single Pole Single Throw) is an electromechanical switch that uses a coil and contacts to control one circuit with a simple ON/OFF operation. It allows low-power signals to switch higher-power loads safely and efficiently. | |
| SPST Switch | A Single-Pole, Single-Throw switch. It is the simplest on/off switch, controlling one circuit with two terminals. It either makes (ON) or breaks (OFF) the connection in a single wire. | |
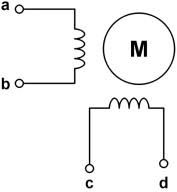 |
Stepper Motor | A brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a number of equal steps. It can be precisely controlled to move and hold at one of these steps without a feedback sensor. |
 |
Terminal Point | A point in a circuit where a connection can be made, often with a screw or clamp. It is a physical access point for connecting wires to a device or piece of equipment. |
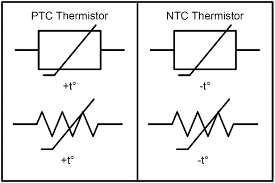 |
Thermistor (NTC/PTC) | A temperature-sensitive resistor. An NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) thermistor’s resistance decreases as temperature rises. A PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) thermistor’s resistance increases as temperature rises. Used for temperature sensing and current limiting. |
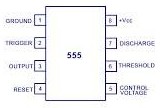 |
Timer IC Symbol | Represents a specific type of IC, like the classic 555 timer, designed to generate precise time delays or oscillations. The internal circuitry is abstracted for simplicity in a schematic. |
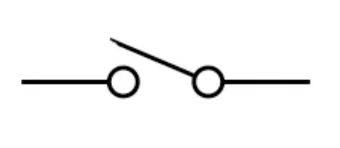 |
Toggle Switch | A common type of switch operated by a mechanical lever or “toggle” that is moved back and forth to open or close one or more circuits. SPST, SPDT, etc., can all be toggle switches. |
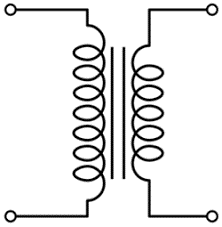 |
Transformer | A component that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. It consists of two or more coils wound on a common core and is used to step up or step down AC voltages. |
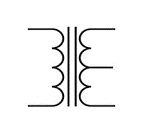 |
Transformer (Center-tapped) | A transformer with a connection (tap) brought out from the center of the secondary winding. This creates two equal output voltages that are 180 degrees out of phase, commonly used in full-wave rectifier circuits and audio amplifiers. |
 |
Trimmer Resistor | A small potentiometer designed for infrequent adjustment, often used for calibration or fine-tuning a circuit after it has been manufactured. It is typically adjusted with a small screwdriver and is not intended for user access. |
 |
Tri-state Buffer | A special type of buffer that has a third output state in addition to HIGH and LOW: a high-impedance (Hi-Z) state. In the Hi-Z state, the output is effectively disconnected from the circuit. |
| Tunnel Diode | A diode that exhibits a property called “negative resistance” due to quantum tunneling. It can operate at very high frequencies and is used in oscillators and microwave amplifiers. | |
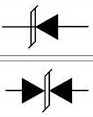 |
TVS Diode | A Transient Voltage Suppression diode is designed to protect electronics from voltage spikes and transients (like ESD). It reacts very quickly to clamp the voltage to a safe level. |
| Varactor / Varicap Diode | A diode that acts as a voltage-controlled capacitor. Its capacitance changes with the applied reverse bias voltage. It is used in electronically tuned circuits, such as voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs). | |
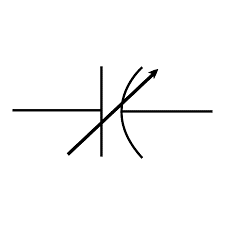 |
Variable Capacitor | A capacitor whose capacitance can be mechanically adjusted. This is typically achieved by moving a set of plates relative to another set. Often used in older radio tuners for selecting different frequencies. |
 |
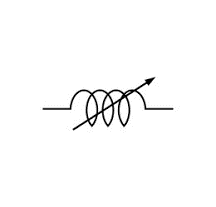
Variable Inductor | An inductor whose value can be adjusted, usually by moving a core in or out of the coil. This allows for the tuning of resonant circuits in applications like radio frequency (RF) transmitters and receivers. |
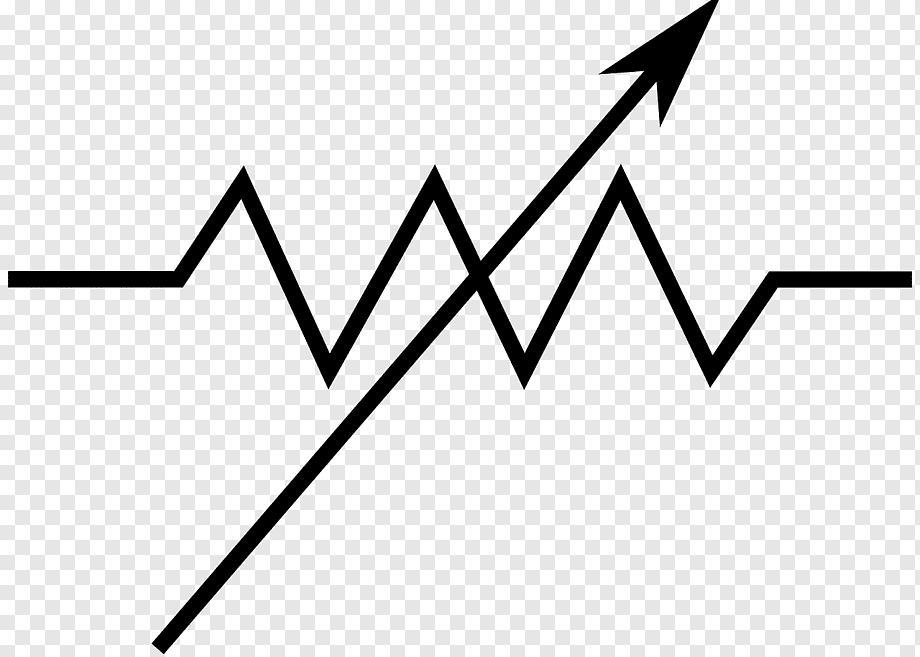 |
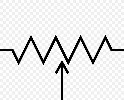
Variable Resistor / Rheostat | A resistor whose electrical resistance can be adjusted manually. A rheostat is typically used to control high currents, often with two terminals, while a general variable resistor may use three. The arrow represents the movable wiper contact. |
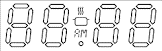 |
VFD Display | A Vacuum Fluorescent Display. It produces a bright blue-green light by exciting a phosphor coating with electrons. Known for high brightness and wide viewing angle, often used in car stereos and appliances. |
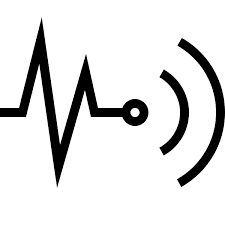 |
Vibration Sensor | A device that detects mechanical vibrations or shocks. It can be a simple switch that closes under shock or a more complex piezoelectric sensor that generates a voltage from vibration. |
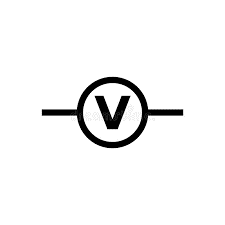 |
Voltmeter | An instrument used for measuring the electrical potential difference (voltage) between two points in an electric circuit. It is always connected in parallel with the component whose voltage is being measured. |
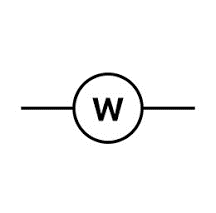 |
Wattmeter | An instrument used to measure the electrical power (in watts) consumed by an electrical circuit. Power is the product of voltage and current, so a wattmeter typically has both voltage and current sensing elements. |
| Wire Connection (Node) | A dot placed at the intersection of two or more lines on a schematic to indicate that the wires are electrically connected at that point. | |
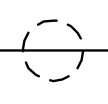
| Wire Crossover (Not Connected) | A specific symbol used to unambiguously show that two wires cross on the schematic without making an electrical connection. This prevents confusion with a connection dot. | |
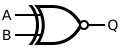 |
XNOR Gate | An Exclusive-NOR gate. Its output is HIGH (1) if the number of HIGH inputs is even. For two inputs, the output is HIGH only when the two inputs are the same. It acts as an equality detector. |
| XOR Gate | An Exclusive-OR gate. Its output is HIGH (1) if the number of HIGH inputs is odd. For two inputs, the output is HIGH only when the two inputs are different. | |
| Zener Diode | A special diode designed to operate reliably in the reverse breakdown region. It maintains a nearly constant voltage across its terminals, making it ideal for voltage regulation and reference circuits. |